
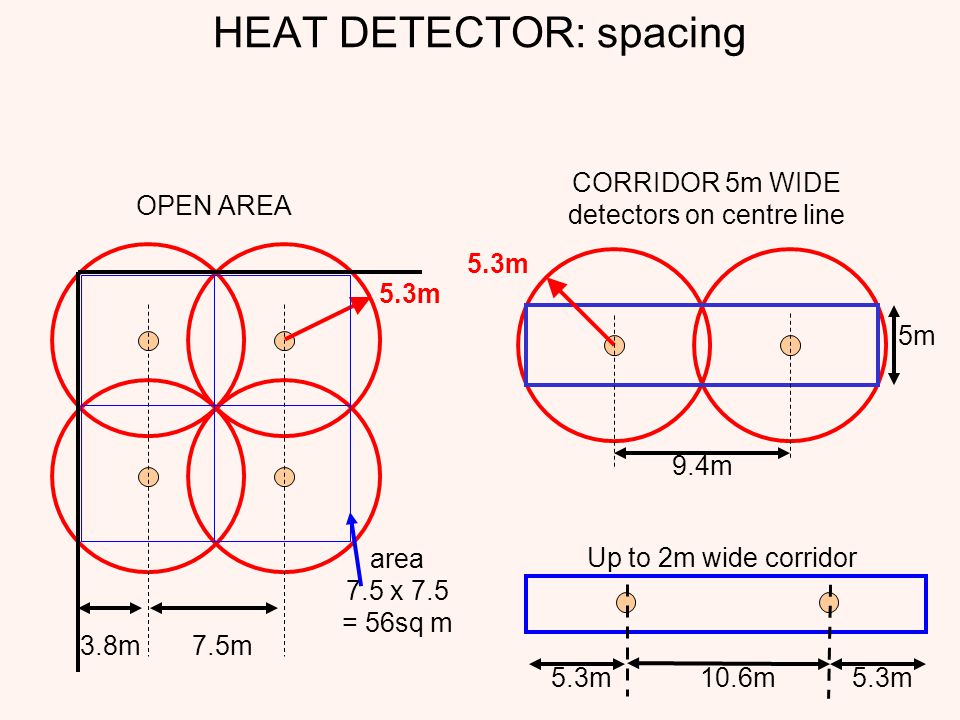
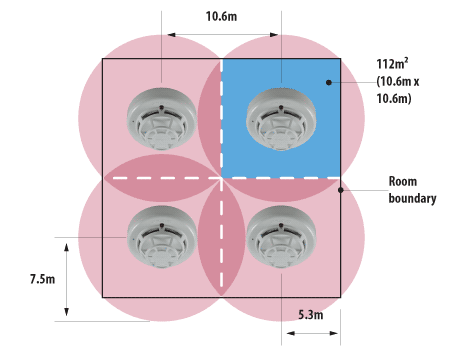
For general area coverage with smoke detectors will be m2. Chapter of NFPA requires that spacing be based on manufacturer’s recommendations. With heat detectors this figure is 7. The coverage of smoke detector is a circle with diameter = meters and for heat detector d=.
The distance between the smoke detector and another smoke detector =. Heat Detector’s Circle of Coverage Since all of the area within the detector’s circle of coverage is suitable for detecting a fire, the shape and dimensions of the detector coverage “square” in Figure may be modified. If rapid response to fire is vital, rate-of-rise heat detectors are an ideal solution where rapid temperature increases would only be caused by a fire emergency. Combination heat detectors provide both fixed and rate-of-rise detection. This enables the heat detector to communicate an alarm to the central control panel prior to reaching its fixed set point for high rates of rise, providing a timely response to both rapid and slow temperature increases. When mounted on a flat ceiling, smoke detection devices have an individual coverage of 7. However these radii must overlap to ensure there are no ‘blind spots’.
Therefore individual coverage can be represented by a square measuring 10. To ensure complete coverage for square layouts, spacings between detectors and walls should be reduced to 5m for a smoke detector and 3. They are placed at keep points around sleeping quarters, stairwells, and access halls to detect smoke only at those locations. Photoelectric smoke detectors send out a beam of light to check for smoke on a vertical or horizontal beam that is quite narrow (depends on mount).
Why to use a heat detector instead of a smoke detector? What is the most sensitive heat detector? Where is heat detector are best used? Is it required to use heat detectors for kitchens? For additional coverage in a system, know that heat detectors are relatively slow and react only to established fires.
The National Fire Alarm Code advises that detectors having fixed-temperature or rate-compensated elements must be selected so the temperature rating is at least 20°F above the maximum expected ambient temperature at the ceiling. The code recommends that detectors be selected to minimize this temperature difference to reduce response time. Higher ceilings may adversely affect detection time.

Earlier detection may be obtained by reducing the spacing between sensors. Microprocessor-controlled monitoring of the heat sensor, software and hardware. Early fire detection with low risk of false alarms. Application-specific configuration of signal processing.
Smoke Detectors versus Heat Detectors – What ’s the difference? The 3Series rate-anticipation heat detector respond and activate the fire alarm immediately whenever the ambient temperature reaches the preset temperature setting. Under rapid heat rise conditions, the rate-anticipation feature enables the detector to respond one to three degrees ahead of the setting. The range, which includes an optical detector , a photo-thermal detector and a heat detector , are ideal for the commercial sector and can be used in a variety of applications.
Detector , it will automatically realign itself to ensure optimum alignment following building movement. End to End The Transmitter (Tx) and the Receiver (Rx) are installed at each end of the area to be protecte up to 1metres apart. A heat detector is a fire alarm device designed to respond when the convected thermal energy of a fire increases the temperature of a heat sensitive element. The thermal mass and conductivity of the element regulate the rate flow of heat into the element.
All heat detectors have this thermal lag. Heat detectors have two main classifications of operation, rate-of-rise and fixed temperature. The heat detector is used to help in the reduction of property damage.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.